🌱 Difference Between Plant and Animal Cells Explained
Every living organism is made up of tiny units called cells — the building blocks of life.
But did you know that plant cells and animal cells, though both eukaryotic, have several important differences?
In this post, we’ll break down the key differences, structure, and functions of each type — in a way that’s easy to understand and perfect for students or curious readers.
🧫 What Is a Cell?
A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of life.
All plants and animals are made of cells, but their structure and components vary according to their roles.
🌿 What Is a Plant Cell?
Plant cells are generally larger and rectangular in shape.
They have a cell wall made of cellulose, which provides support and rigidity.
Plant cells also contain chloroplasts, allowing them to perform photosynthesis — the process of making food using sunlight.
Main Features of Plant Cells:
- Have a cell wall
- Contain chloroplasts (for photosynthesis)
- Large central vacuole
- Usually rectangular in shape
🐾 What Is an Animal Cell?
Animal cells are usually smaller and round in shape.
They lack a cell wall but have a flexible cell membrane.
Animal cells don’t perform photosynthesis, but they have specialized organelles like centrioles and lysosomes that help in cell division and waste breakdown.
Main Features of Animal Cells:
- No cell wall
- No chloroplasts
- Small vacuoles
- Round or irregular shape
🔬 Key Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Present | Absent |
| Shape | Rectangular | Round or irregular |
| Chloroplasts | Present (for photosynthesis) | Absent |
| Vacuole | Large central vacuole | Small or many vacuoles |
| Centrioles | Absent (except in some lower plants) | Present |
| Energy Production | From sunlight (photosynthesis) | From food (cell respiration) |
| Lysosomes | Rare | Common |
READ DETAILS ATBasic unit of Life
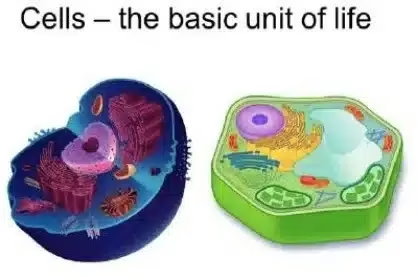
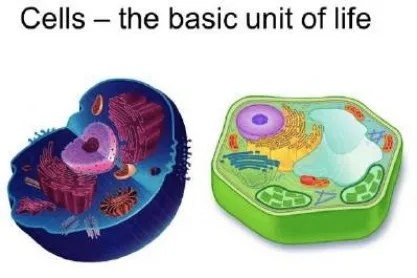
🧠 Similarities Between Plant and Animal Cells
Despite their differences, both have several common features:
- Cell membrane controlling entry/exit of substances
- Nucleus containing DNA
- Cytoplasm where reactions occur
- Mitochondria producing energy
- Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus for protein and lipid synthesis
🌞 Why These Differences Matter
Plants need to make their own food and remain upright — that’s why they have chloroplasts and a cell wall.
Animals, on the other hand, need mobility and flexibility — hence they have no rigid cell wall but more energy-consuming organelles like mitochondria.
💬 Conclusion
Both plant and animal cells are essential to life, but they are adapted to their specific roles.
Plant cells build their own food through photosynthesis, while animal cells rely on consuming energy sources.
Understanding their differences helps us appreciate how diverse and specialized life can be — even at the microscopic level.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large vacuole, while animal cells do not.
Because they perform photosynthesis — making food from sunlight.
No, they only have a flexible cell membrane.
The mitochondrion, found in both plant and animal cells.
No, they depend on external food sources for energy.

Cells are sooooo complex. Thank you for this post.
Absolutely! Cells are incredibly complex and fascinating 🤯🔬
Thanks so much for reading.If you enjoyed the post, do share it with others — your share helps us reach more curious minds. 💙🙌