🧠 Blood Supply of the Brain: The Hidden Network(circle of willis) That Keeps You Alive (Explained Simply!)
Did you know? Your brain makes up just 2% of your body weight, yet it consumes 20% of all the oxygen in your blood.circle of willis
And here’s the shocking part:
⏳ Consciousness stops in just 10 seconds if blood flow stops.
💀 Irreversible brain damage begins in just 4 minutes.
This is why understanding the blood supply of the brain is not just important—it’s life-saving.
In this article, we break down the entire system into simple language while keeping it medically accurate. Perfect for MBBS students, NEET PG aspirants, and science enthusiasts.
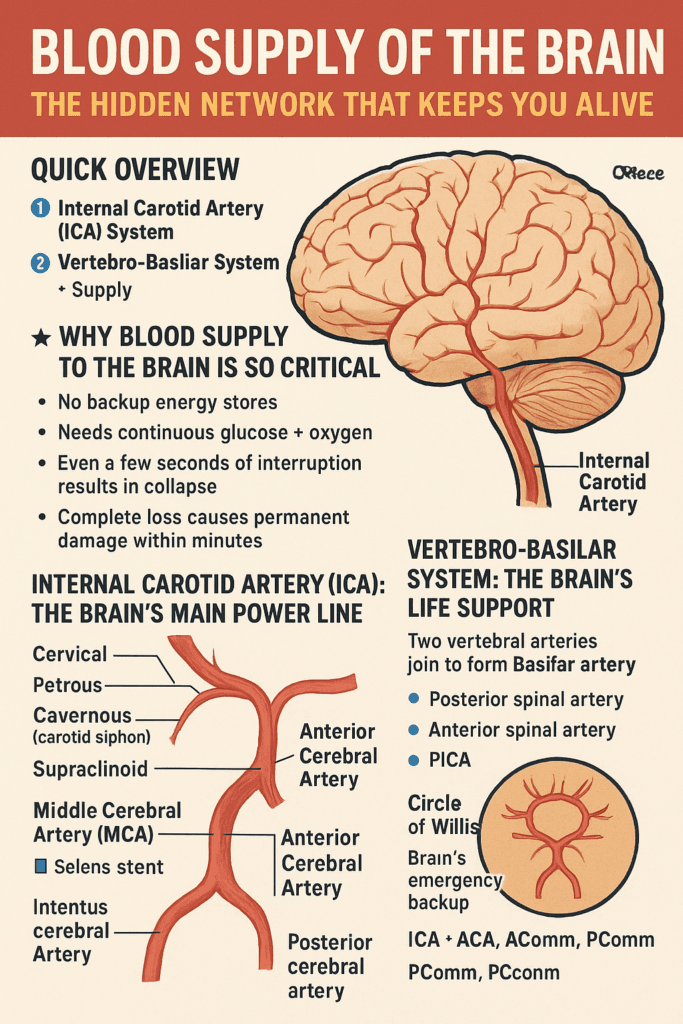
⭐ Quick Overview
The brain is supplied by two major arterial systems:
1️⃣ Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) System
Supplies:
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Lateral temporal lobe
- Majority of internal capsule
- Anterior part of thalamus
2️⃣ Vertebro-Basilar System
Supplies:
- Brainstem (midbrain, pons, medulla)
- Occipital lobe
- Inferior surface of temporal lobe
- Cerebellum
- Posterior part of thalamus
Together, they form a protective network called the Circle of Willis, the brain’s emergency bypass mechanism.
🔥 Why Blood Supply to the Brain Is So Critical
- No backup energy stores
- Needs continuous glucose + oxygen
- Even a few seconds of interruption results in collapse
- Complete loss causes permanent damage within minutes
This is why stroke happens instantly and spreads rapidly.
🩺 Internal Carotid Artery (ICA): The Brain’s Main Power Line
ICA has four parts:
- Cervical
- Petrous
- Cavernous (carotid siphon)
- Supraclinoid — the most important intracranial portion
It ultimately divides into:
- Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
- Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)
Major branches include:
- Ophthalmic artery
- Posterior communicating artery
- Anterior choroidal artery
🧩 Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)
Supplies:
- Medial frontal lobe
- Medial parietal lobe
- Cingulate gyrus
- Paracentral lobule
Clinical:
- ACA occlusion → contralateral leg weakness > arm
🧩 Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
The largest and most important branch.
Supplies:
- Lateral surface of frontal, temporal, parietal lobes
- Broca’s & Wernicke’s areas
- Motor cortex for face & upper limb
- Important sensory areas
Clinical:
- MCA occlusion → face + arm weakness, aphasia, sensory loss
- Lenticulostriate arteries → “arteries of stroke”
🧩 Anterior Choroidal Artery
Supplies:
- Optic tract
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
- Posterior limb of internal capsule
Nicknamed the artery of cerebral thrombosis.
🧠 Vertebro-Basilar System: The Brain’s Life Support
Two vertebral arteries join to become the Basilar artery.
⭐ Vertebral artery branches:
- Posterior spinal artery
- Anterior spinal artery
- PICA (Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery)
⭐ Basilar artery branches:
- AICA
- Superior cerebellar artery
- Pontine branches
- Posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
🧩 Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA)
Supplies:
- Occipital lobe
- Inferior temporal lobe
- Visual cortex
Clinical:
- PCA occlusion → contralateral homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing
🌀 Circle of Willis: Brain’s Emergency Backup
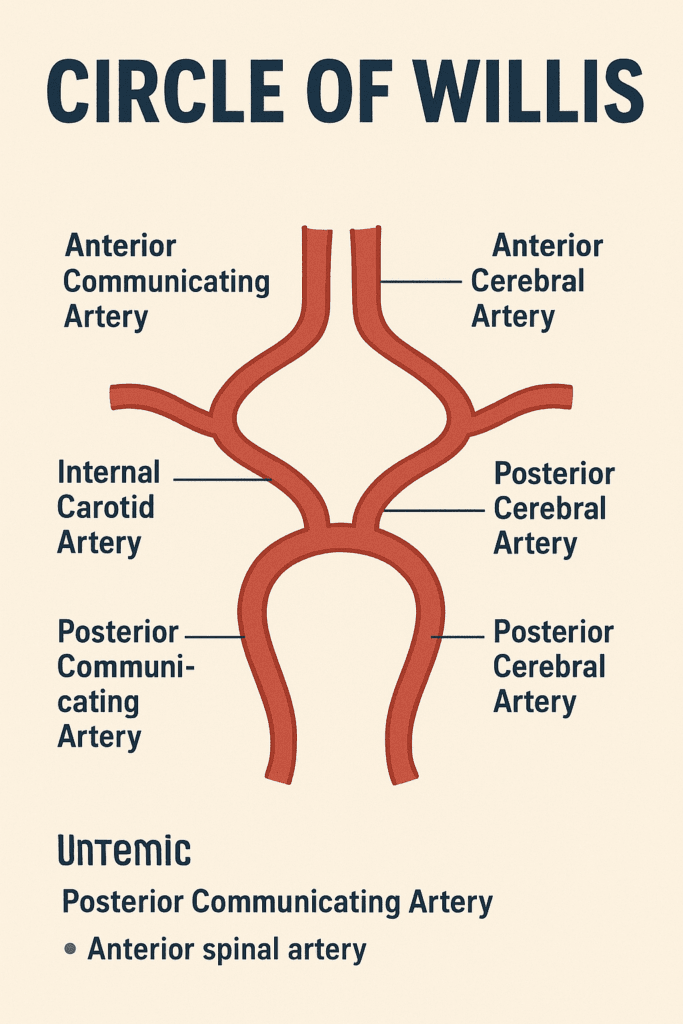
A vital arterial ring that connects:
- ICA system
- Basilar system
Acts as a bypass during vessel blockage.
Formed by:
- ICA
- ACA
- AComm
- PComm
- PCA
🩸 Venous Drainage of the Brain (Simplified)
Brain veins are:
- Thin-walled
- Valve-less
- Drain into dural venous sinuses
⭐ Types
- Superficial cerebral veins
- Deep cerebral veins
- Cerebellar veins
- Brainstem veins
Important veins:
- Superior cerebral veins → Superior sagittal sinus
- Superficial middle cerebral vein → Cavernous sinus
- Deep middle cerebral vein → Basal vein
- Internal cerebral veins → Great cerebral vein (of Galen)
🚨 Stroke Patterns Made Easy
| Artery Blocked | Key Deficit |
|---|---|
| ACA | Leg weakness |
| MCA | Face & arm weakness, aphasia |
| PCA | Visual field loss |
| ICA | Massive contralateral deficits |
| Vertebrobasilar | Bilateral symptoms, brainstem signs |
🌟 High-Intent Keywords Included
- blood supply of the brain
- internal carotid artery branches
- vertebrobasilar circulation
- circle of willis explained
- MCA stroke symptoms
- ACA vs MCA vs PCA
- venous drainage of brain simplified
- neuroanatomy blood supply
❓ FAQs
The Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) supplies the largest cortical territory
The lenticulostriate arteries of MCA are most vulnerable.
Loss of vision on one side — homonymous hemianopia.
It provides collateral blood flow during blockage.
📌 Final Words: The Brain’s Blood Supply Is a Masterpiece of Design(circle of willis)
Every second, millions of neurons depend on uninterrupted blood flow.
One blockage can change everything — which is why understanding this system matters deeply for students, doctors, and anyone curious about the brain.