How Pain Actually Works in the Body
😣 Why Does Pain Feel So Real?
Touch a hot pan. Step on a sharp object. Twist your ankle.
Within milliseconds, your body reacts — sometimes before you even realize what happened.
But have you ever wondered…
👉do you know How does pain actually work inside your body?
👉 Why does emotional pain sometimes hurt physically?
👉 Why does chronic pain continue even after healing?
Let’s break it down in simple, mind-blowing science.
⚡ Step 1: Pain Begins with Special Sensors (Nociceptors)
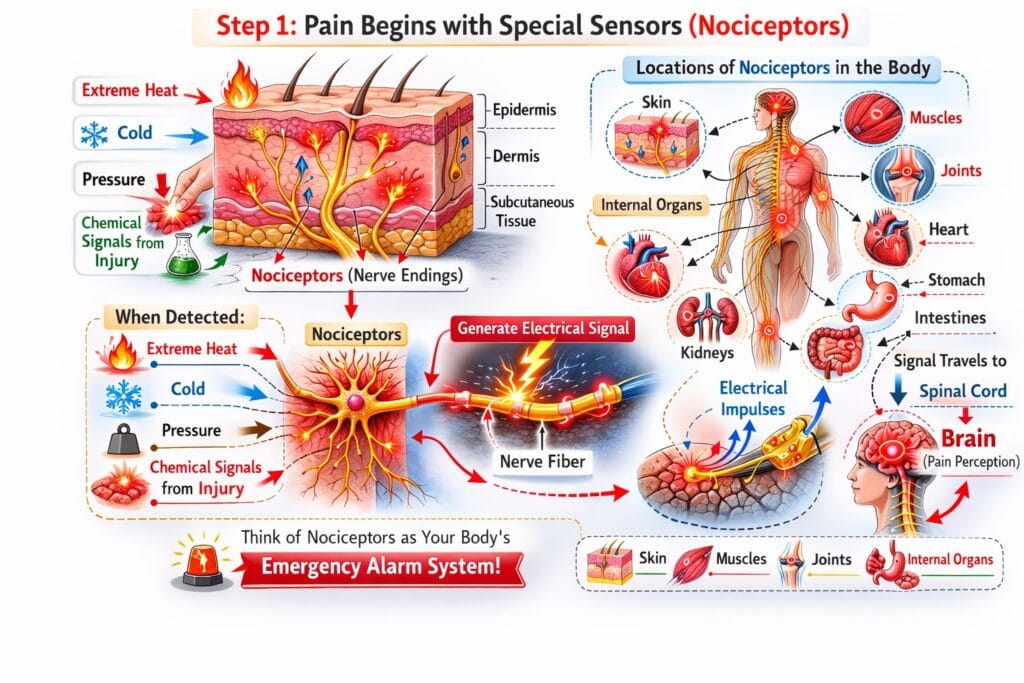
Pain starts with specialized nerve endings called nociceptors.
These tiny sensors are located in:
- Skin
- Muscles
- Joints
- Internal organs
When they detect:
- Extreme heat 🔥
- Cold ❄️
- Pressure
- Chemical signals from injury
They generate an electrical signal.
💡 Think of nociceptors as your body’s emergency alarm system.
🚀 Step 2: The Signal Travels Through Your Nervous System
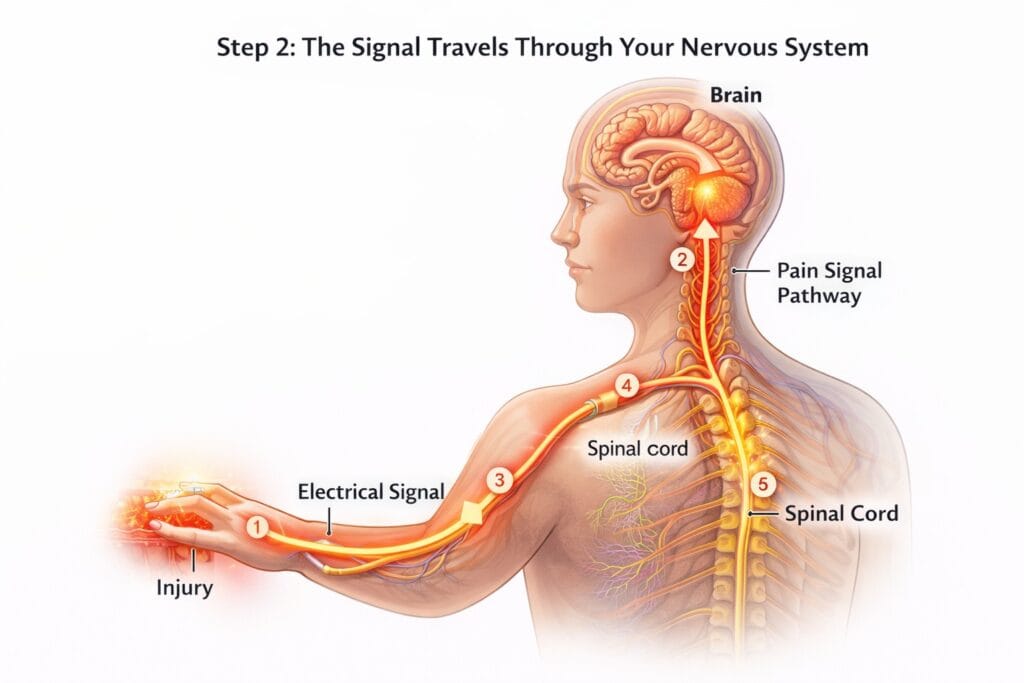
Once activated, the signal travels:
- From injury site
- Through peripheral nerves
- Into the spinal cord
- Up to the brain
1️⃣ Injury Happens (At the Hand)
On the left side, you see a hand touching something hot.
- Tissue damage occurs.
- Pain receptors (nociceptors) are activated.
- They generate an electrical signal.
This is the beginning of the pain pathway.
⚡ 2️⃣ Electrical Signal Travels Through Peripheral Nerves
The glowing orange line in the arm represents:
🟠 A nerve fiber carrying an electrical impulse
This signal travels quickly through:
- Peripheral nerves
- Toward the spinal cord
This happens in milliseconds.
🧠 3️⃣ Signal Reaches the Spinal Cord
The signal enters the spinal cord.
Here two things can happen:
🔁 Reflex Action
Your spinal cord can immediately send a signal back to your muscles to pull your hand away — even before your brain fully processes pain.
That’s why you react instantly.
⬆ 4️⃣ Signal Travels Up to the Brain
The highlighted vertical pathway in the neck shows the signal traveling upward through the spinal cord to the brain.
This pathway is often called the pain signal pathway.
🧠 5️⃣ Brain Processes the Pain
The brain area glowing in orange represents where pain is interpreted.
Here the brain:
- Identifies location (your hand)
- Determines intensity
- Adds emotional meaning
- Makes you consciously “feel” pain
Important truth:
👉 The injury happens in your hand.
👉 But the experience of pain is created in your brain.
🔬 Given Image Teaches
✔ Pain starts at the injury
✔ Travels as an electrical signal
✔ Passes through the spinal cord
✔ Is finally interpreted in the brain
Without the brain, there is no pain sensation — only signals.
💡 Simple Summary
Pain is like a message:
Injury ➝ Nerve ➝ Spinal Cord ➝ Brain ➝ You Feel Pain
Your nervous system works like a super-fast communication network protecting your body.
This all happens in a fraction of a second.
Sometimes, your spinal cord reacts before your brain even processes pain. That’s why you pull your hand away instantly from a hot surface.
This is called a reflex action.
READ human sneeze reflex
🧠 Step 3: Your Brain Creates the Feeling of Pain
Here’s the surprising truth:
👉 Pain is not in your finger.
👉 Pain is not in your ankle.
👉 Pain is created in your brain.
Different parts of the brain interpret the signal, especially areas like:
- Thalamus – relays pain messages
- Somatosensory cortex – identifies location
- Amygdala – adds emotional response
That’s why:
- The same injury can feel different on different days
- Stress increases pain
- Fear makes pain worse
Your brain decides how intense pain feels.
🧪 Types of Pain (And Why They Feel Different)
1️⃣ Acute Pain
Short-term pain from injury or damage.
Example: Cut, burn, fracture.
It’s protective and useful.
2️⃣ Chronic Pain
Pain lasting more than 3 months.
Sometimes tissues heal — but the brain keeps sending pain signals.
Conditions like chronic back pain or migraines fall here.
3️⃣ Referred Pain
Pain felt in a different place than the source.
Example:
Heart attack pain felt in left arm.
🤯 Why Emotional Pain Feels Physical
Heartbreak. Grief. Rejection.
Brain scans show emotional pain activates similar regions as physical pain.
That’s why phrases like “broken heart” feel real.
The brain processes social rejection using some of the same neural pathways as physical injury.
Pain isn’t just physical — it’s deeply emotional.
🧬 Why Some People Feel More Pain Than Others
Pain tolerance depends on:
- Genetics
- Mood
- Past experiences
- Sleep quality
- Inflammation
- Mental health
Two people with the same injury can report very different pain levels.
Your brain modifies pain signals constantly.
💊 How Painkillers Work
Pain medications work in different ways:
- Some block inflammatory chemicals
- Some reduce nerve signaling
- Some change how the brain interprets pain
For example:
Common painkillers reduce prostaglandins — chemicals that increase pain sensitivity.
But they don’t “remove” pain — they interrupt the signal.
⚠️ When Pain Becomes a Problem
Pain is protective.
But when it becomes constant, it turns from a warning system into a malfunctioning alarm.
Chronic pain can:
- Affect sleep
- Reduce immunity
- Increase stress hormones
- Impact mental health
Understanding pain helps reduce fear — and fear itself amplifies pain.
🔬 The Most Powerful Truth About Pain
Pain is not just damage.
It is a brain-generated protective experience.
yes Sometimes it protects you.
Sometimes it overreacts.
Sometimes it lingers.
But it always has a purpose.
📌 Quick Summary
- Pain begins with nociceptors
- Signals travel through nerves to the spinal cord
- The brain creates the pain experience
- Emotions influence pain intensity
- Chronic pain involves brain rewiring
Your body isn’t trying to hurt you.
It’s trying to protect you.
Read also How the Human Brain Works While You Sleep (Shocking Science)
❓ FAQ
Yes. Chronic pain can occur even after tissues heal due to brain sensitivity changes.
Stress hormones increase inflammation and make the nervous system more sensitive.
Interestingly, the brain itself has no pain receptors — but it creates the experience of pain.
If ScienceGajab helped you learn something new, please support us — even a small contribution makes a big difference.Your small contribution helps us create more free, quality science content for everyone.
Even ₹10 (0.11$) makes a difference.
You can support us instantly by scanning the UPI QR code below .

Thank you for being part of the ScienceGajab family.