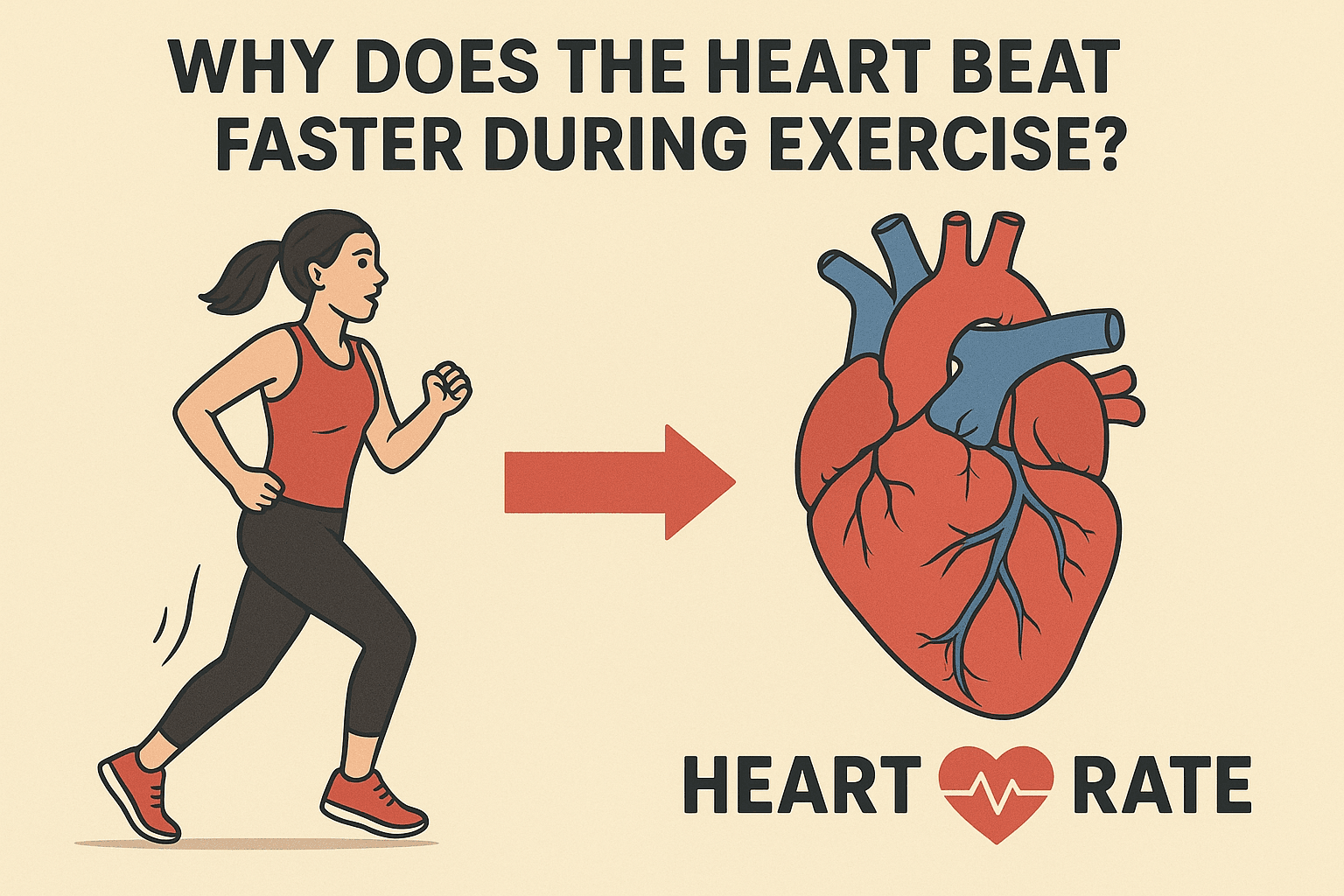
❤️ Why Does the Heart Beat Faster During Exercise?
why heart beats faster during exercise
Have you ever noticed your heart pounding faster when you run, climb stairs, or dance? That’s not just random — it’s your body’s intelligent way of keeping up with your muscles’ needs.
In this post, we’ll explore the science behind your racing heartbeat, how it helps your body, and why it’s actually a sign of good health.
🫀 What Happens to the Heart During Exercise?
When you start exercising, your muscles need more oxygen and nutrients to produce energy.
Your heart responds immediately by:
- Pumping faster to deliver more oxygen-rich blood
- Increasing blood flow to active muscles
- Removing waste products like carbon dioxide and lactic acid
💨 Why Does the Heart Rate Increase?
The brain detects changes in your muscles through chemical signals. It then sends messages to your heart via the nervous system, telling it to beat faster and stronger.
Here’s what happens step by step:
- Muscles use more oxygen and produce carbon dioxide.
- Sensors in blood vessels detect the increase in CO₂.
- Brain’s cardiovascular center activates.
- Heart rate increases to maintain oxygen supply.
⚡ How Much Can the Heart Rate Increase?
A healthy adult’s resting heart rate is around 60–100 beats per minute (bpm).
During intense exercise, it can rise to:
- 120–160 bpm for moderate workouts
- 170–190 bpm for vigorous activity (like sprinting or HIIT)
🔢 Formula to estimate your maximum heart rate:
👉 220 – your age
Example: If you’re 25 years old → 220 – 25 = 195 bpm (your approximate max heart rate).
🧠 Why Is a Faster Heartbeat Good During Exercise?
When your heart beats faster, it’s working hard to supply oxygen and remove toxins.
This helps in:
- Improving cardiovascular fitness
- Strengthening the heart muscles
- Enhancing blood circulation
- Training your body to handle physical stress better
⚕️ What Happens After You Stop Exercising?
When you stop, your body’s oxygen demand decreases. The heart rate gradually slows down as the body returns to its resting state.
This recovery rate is an important measure of heart health —
👉 The faster your heart rate returns to normal, the healthier your heart is.
🩺 Tips for a Healthy Heart
- Do at least 30 minutes of exercise daily (walking, jogging, cycling).
- Eat heart-friendly foods — fruits, nuts, and whole grains.
- Avoid smoking and limit junk food.
- Get regular medical check-ups.
- Practice deep breathing or meditation for stress relief.
💬 Conclusion
Your heart beating faster during exercise is a normal and healthy reaction.
It means your heart is efficiently responding to your body’s increased energy needs.
Over time, regular exercise makes your heart stronger — so it can pump more blood with fewer beats.
So next time your heart races, remember — it’s proof that your body is alive, active, and working perfectly! ❤️
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
Because your muscles need more oxygen and energy, so your heart pumps faster to deliver oxygen-rich blood.
It usually ranges between 120–170 bpm, depending on age and activity intensity.
Subtract your age from 220 (e.g., 220 – 30 = 190 bpm).
If it exceeds your maximum limit, stop and rest. It might cause dizziness or strain on the heart.
Yes, over time, a stronger heart can pump more efficiently, leading to a lower resting heart rate.