Your body is responsible for thousands of extremely complex and fascinating processes every second. Here’s what you should know.
1.The human body has 12 systems

The human body’s 12 systems work together to ensure that we stay alive, healthy, and thrive:
- The cardiovascular (or circulatory) system transports blood, oxygen, and nutrients throughout the body.
- The digestive system takes in and processes food, and expels waste.
- The endocrine system produces hormones that regulate metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sexual reproduction, sleep, and mood.
- The immune system fights infection caused by pathogens, like bacteria and viruses.
- The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of your body, in other words: your skin! And it protects your soft and squishy interior from damage by external dirt, pathogens, and trauma.
- The lymphatic system is part of the immune system and complementary to the circulatory system. It keeps body fluid levels in balance and defends against infections.
- The muscular system facilitates movements of our bodies, from reaching for the remote control to smashing out an intense workout in the boxing ring.
- The nervous system, which consists of your brain, the spinal cord, and all the nerves throughout your body, controls movement, balance, the five senses, thought processes, and awareness.
- The reproductive system—*insert opening riff to Marvin Gaye’s Let’s get it on—allows us to uhh make babies.
- The respiratory system facilitates breathing; more specifically, the intake of oxygen and expulsion of carbon dioxide.
- The skeletal system provides a strong and durable framework upon which all your meat hangs, while helping to protect your delicate internal organs.
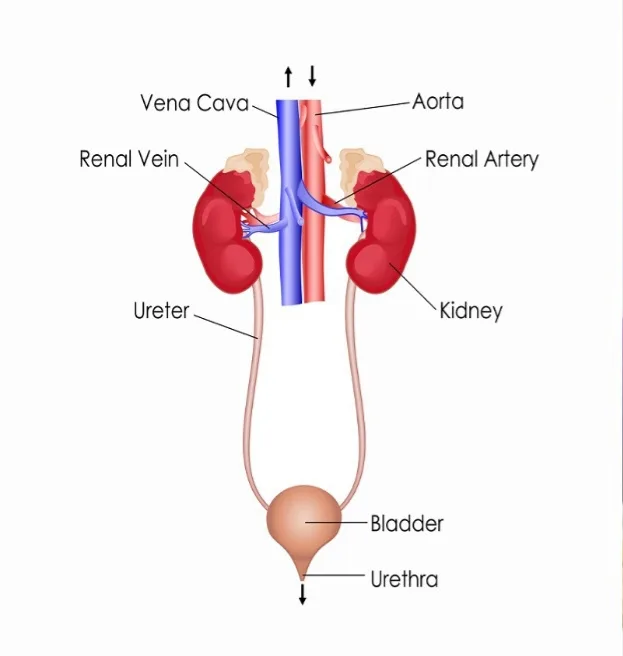
- The urinary system expels waste and extra water that the body doesn’t need.
- these are human biology basics
2. There are four blood groups:
A, B, AB, and O Your lettered blood type is determined by which antibodies are in your plasma and which antigens are present in your red blood cells. (Antibodies are blood proteins, while antigens activate an immune response and control what enters and exits a cell.)Additionally, each blood group can be either positive or negative, resulting in eight possible blood types. The +/- part of a person’s blood type is determined by the presence (or absence) of a third antigen called the Rh factor.
3. Our DNA is stored in 23 pairs of chromosomes within the nucleus of every cell in our body:
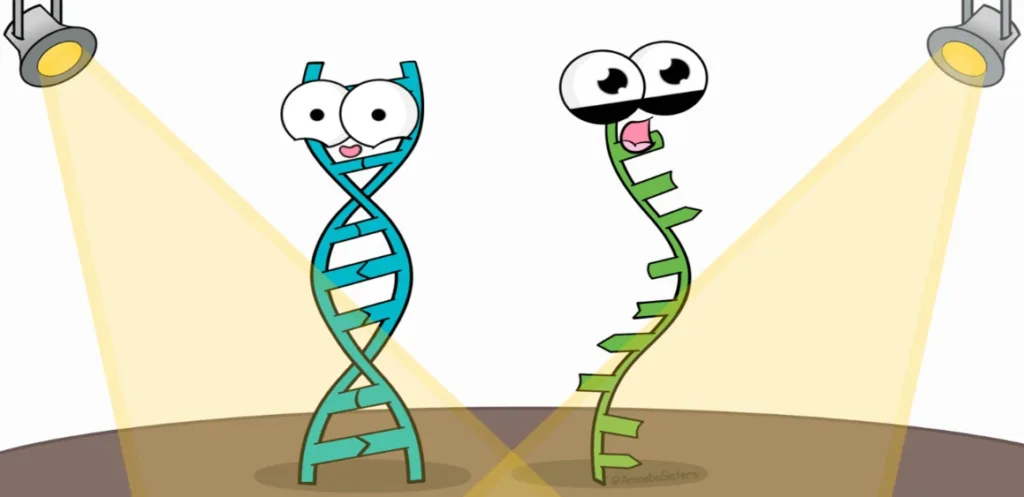
Every cell in your body, from your hair follicles to your toenails—has a full set of chromosomes, which contains all the genetic material needed to determine the makeup of our entire bodies. That’s why animals can be cloned using just one cell.
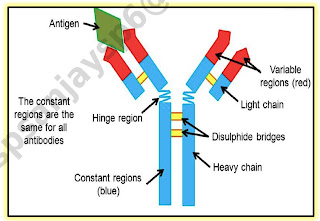
4. Our immune system fights off infection mostly through the use of antibodies and microphages
Upon detecting a pathogen, macrophages (or white blood cells) will surround and immobilize it, literally consuming it with their bodies. Antibodies, on the other hand, are the high-powered weaponry made by white blood cells to destroy the invaders( human biology basics)
5.Our appendix does actually still have a purpose ;Researches shows many good bacteria lives here
6. We still aren’t 100% sure why people yawn
(Try not to yawn while reading this.)
In the animal kingdom, yawning can also be a sign of aggression—particularly amongst apes and monkeys. But with humans, it’s usually just because we feel tired. So, if your date is yawning excessively, you might try to change the conversation, suggest a walk outside, or fire up Tinder again.
human biology basics
7. Nearsightedness(myopia) and farsightedness(hypermetropia) are caused by defects in the shape of our eyeballs
If you can’t see near or far objects, your eyeballs are shaped weird, which, while an expensive problem to have, makes you special (just like everybody else who has to wear eyeglasses).
8. The red color of our blood is caused by the shape of the structure created when iron and oxygen bond with hemoglobin
Some people assume that blood is red because of all the iron in it, kind of like why rust is red. But it’s a little more complex than that. The red color of blood is created because the iron in your hemoglobin is bound in a ring of atoms called porphyrin. This structure has a shape that makes the blood appear red. When oxygen binds to the porphyrin ring, it changes the shape, making our red blood cells appear an even more vivid shade of red.
9.Our body has more sense organ(>5)
Balance: Essentially your brain’s perception of which way is up.
Temperature: Or, if we’re to get real nerdy, thermoreception is your body’s sensation and perception of hot and cold.
Proprioception: Spatial body awareness. What’s that? Close your eyes and touch your nose. That’s what proprioception is.
Pain: Staple your figure to your desk. That’s what pain is. Just kidding. ⚠️Don’t do that.⚠️
10. The liver has over 500 functions
All the blood leaving the stomach and intestines passes through the liver, where it is processed, broken down, and balanced so that it can be returned to the body fresh and clean. The liver also stores important nutrients and glucose (for energy), metabolizes drugs, synthesizes proteins, and aids in metabolism and detoxification. In other words, our liver is one busy, busy organ!
11. The brain works harder while we are asleep than when we are awake
12 Vaccines safely help the body to recognize and fight off infections later in life
13. There are more non-human cells in our body than human ones
Okay, so this one is a little unsettling. Did you know that there are ten times more bacteria cells in our bodies than our own human cells?
14. All body parts can repair themselves (except teeth)
Innate human biology allows us to repair ourselves pretty easily for the most part. Muscle and skin heal, bones can knit back together, and tendons can repair: all of our body parts can heal and regenerate on their own—except teeth. Since dental enamel is not living tissue, it cannot regenerate, even if the injury goes deep enough to damage the living part of the tooth.
15.Heart: The average adult heart beats around 100,000 times a day
These are 15.Human biology basics everyone should know
🧩 introduction to human body for beginners
🧠 Frequently Asked Questions About Human Biology Basics
Q1. What are the basic concepts of human biology?
Human biology covers how the body works — including cells, tissues, organs, and systems such as the heart, brain, lungs, and immune system. It explains how these parts interact to maintain life and health.
Q2. Why is it important to learn human biology?
Understanding human biology helps us know how our body functions, how to stay healthy, and how diseases affect us. It’s the foundation for studying medicine, nursing, and health sciences.
Q3. What is the easiest way to learn human biology?
Start with the basics: body systems, cell structure, and organs. Use visual diagrams, quizzes, and everyday examples to make learning easier and more interesting.
Q4. What are the main systems of the human body?
The major systems are the circulatory, nervous, respiratory, digestive, skeletal, muscular, immune, and reproductive systems. Each works together to keep the body balanced (homeostasis).
Q5. What are some interesting facts about the human body?
The brain contains about 86 billion neurons, the heart beats around 100,000 times per day, and skin is the largest organ — covering nearly 2 square meters in adults!
This was very informative and a pleasant read. Thank you.
Thanks😊