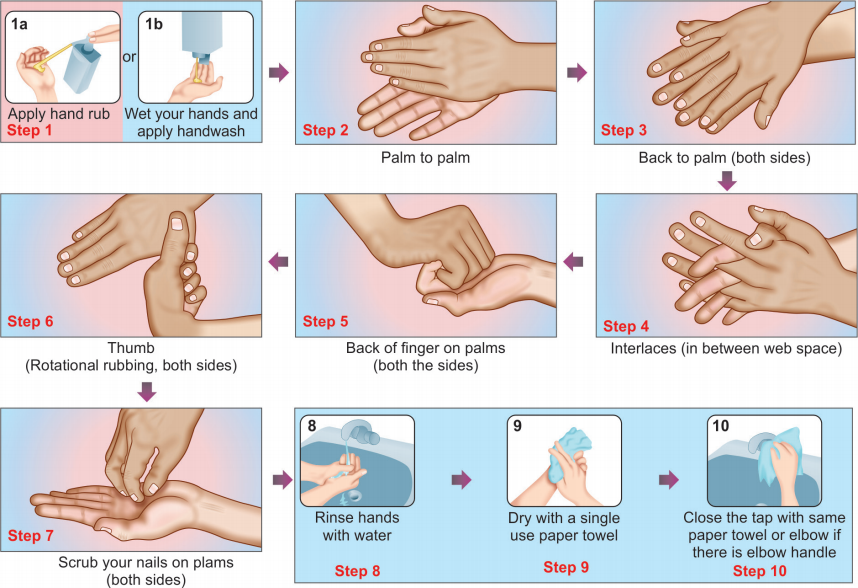
Types of hand hygiene & 7 steps of washing hands

Hand Rub
Alcohol based (70–80% ethyl alcohol) and chlorhexidine (0.5–4%) based hand rubs are available. The duration of contact has to be at least for 20–30 seconds.
Advantage: After a period of contact, it gets evaporated of its own, hence drying of hands is not required separately.
Indications: Hand rub is indicated during routine patient care activities or taking rounds in the wards or ICUs—whenever opportunity for hand hygiene arises, except when the hands are visibly soiled with blood or other specimens.7 steps of washing hands
Hand Wash
Antimicrobial soaps (liquid, gel or bars) are available containing 4% chlorhexidine. If facilities are not available, then even ordinary soap and water can also be used.
The duration of contact has to be at least for 40–60 seconds.
- Hand washing is indicated in the following situations:
- When the hands are visibly soiled with blood, excreta, pus, etc.
- Before and after eating
- After going to toilet
- Before and after shift of the duty
- When giving care to a patient with diarrhea.
Surgical Hand Scrub (3-5 min):
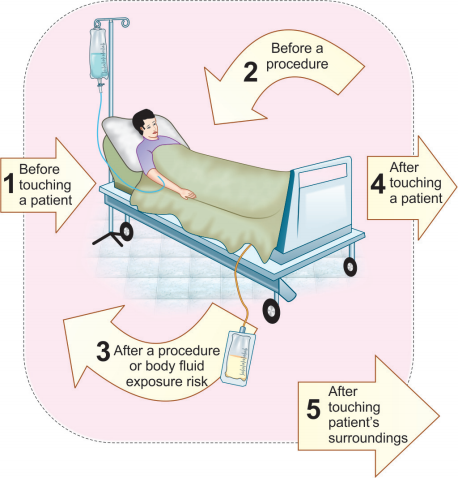
This is indicated prior to any surgical procedure and also in between the cases; using 4% chlorhexidine hand wash.Indications (Five Moments for Hand Hygiene)The WHO has published standard guidelines describing the situations or opportunities when hand hygiene is indicated in healthcare sectors —known as ‘My Five Moments for Hand Hygiene’; which include:
1. Before touching a patient
2. Before clean/aseptic procedures
3. After body fluid exposure/risk
4. After touching a patient
5. After touching patient’s surroundings.
Steps of Hand Rubbing and Hand Washing
WHO has also laid down the guidelines describing the appropriate steps involved for an effective hand rubbing and hand washing